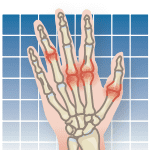
TNF, or tumor necrosis factor, is a substance made by the bodys immune system. People with an immune disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), have excessive amounts of TNF in their bodies. A TNF inhibitor can reduce the amount of TNF to normal levels, helping to control the disease. TNF inhibitors are used in patients with RA who have not responded adequately to traditional therapy, such as methotrexate and plaquenil. Initial improvement tends to occur within a few days, and may continue to increase over a few weeks. Symptoms (pain, stiffness, fatigue) respond more quickly than physical signs (joint swelling). The main side effects of TNF inhibitors are infection and malignancy (especially lymphoma). Both are unusual. The frequency of lymphoma is also slightly increased in RA patients not treated with TNF inhibitors, so the origin of it in individual patients is not entirely clear. Pain at the injection site is common with etanercept (Enbrel) and adalimumab (Humira). Headache occurs occasionally with etanercept and can be severe enough that the drug must be stopped.
To continue reading this article or issue you must be a paid subscriber.
Sign in